Hand Anatomy
The human hand is made up of the wrist, palm, and fingers and consists of 27 bones, 27 joints, 34 muscles, over 100 ligaments and tendons, and many blood vessels and nerves.
The hands enable us to perform many of our daily activities such as driving, writing and cooking. It is important to understand the normal anatomy of the hand to learn more about diseases and conditions that can affect our hands.
Bones of the Hand
The wrist is comprised of 8 carpal bones. These wrist bones are attached to the radius and ulna of the forearm to form the wrist joint. They connect to 5 metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand. Each metacarpal bone connects to one finger at a joint called the metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP joint). This joint is commonly referred to as the knuckle joint.
The bones in our fingers and thumb are called phalanges. Each finger has 3 phalanges separated by two interphalangeal joints, except for the thumb, which has only 2 phalanges and one interphalangeal joint.
The first joint close to the knuckle joint is called the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP joint). The joint closest to the end of the finger is called the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint).
The MCP and PIP joint act like hinges when the fingers bend and straighten.
Soft Tissues of the Hand
Our hand bones are held in place and supported by various soft tissues. These include: articular cartilage, ligaments, muscles and tendons.
Articular cartilages are smooth material that act as shock absorbers and cushion the ends of bones at each of the 27 joints, allowing smooth movement of the hand.
Muscles and ligaments function to control the movement of the hand.
Ligaments are tough rope-like tissues that connect bones to other bones, holding them in place and providing stability to the joints. Each finger joint has two collateral ligaments on either side, which prevents the abnormal sideways bending of the joints. The volar plate is the strongest ligament in the hand. It joins the proximal and middle phalanx on the palm side of the joint and prevents backward bending of the PIP joint (hyperextension).
Muscles of the Hand
Muscles are fibrous tissues that help produce movement. They work by contracting.
There are two types of muscles in the hand:
- Intrinsic muscles are small muscles that originate in the wrist and hand. They are responsible for fine motor movements of the fingers during activities such as writing or playing the piano.
- Extrinsic muscles that originate in the forearm or elbow control the movement of the wrist and hand. These muscles are responsible for gross hand movements. They position the wrist and hand while the fingers perform fine motor movements.
Each finger has six muscles controlling its movement: three extrinsic and three intrinsic muscles. The index and little finger each have an extra extrinsic extensor.
Tendons of the Hand
Tendons are soft tissues that connect muscles to bones. When muscles contract, tendons pull the bones, causing the finger to move. The extrinsic muscles are attached to finger bones through long tendons that extend from the forearm through the wrist. Tendons located on the palm side help in bending the fingers and are called flexor tendons, while tendons on top of the hand called extensor tendons help in straightening the fingers.
Nerves of the Hand
Nerves of the hand carry electrical signals from the brain to the muscles in the forearm and hand, enabling movement. They also carry the senses of touch, pain and temperature back from the hands to the brain.
The three main nerves of the hand and wrist include:
- Ulnar nerve: The ulnar nerve crosses the wrist through an area called Guyon’s canal and branches to provide sensation to the little finger and half of the ring finger.
- Median nerve: The median nerve crosses the wrist through a tunnel called the carpal tunnel. The median nerve provides sensation to the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger and part of the ring finger.
- Radial nerve: The radial nerve runs down the thumb side of the forearm and provides sensation to the back of the hand from the thumb to the middle finger.
All three nerves originate at the shoulder and travel down the arm to the hand. Each of these nerves has sensory and motor components.
Blood Vessels of the Hand
Blood vessels travel beside the nerves to supply blood to the hand. The main arteries are the ulnar and radial arteries, which supply blood to the front of the hand, fingers, and thumb. The ulnar artery travels next to the ulnar nerve through the Guyon’s canal in the wrist. The radial artery is the largest artery of the hand, traveling across the front of the wrist, near the thumb. Pulse is measured at the radial artery.
Other blood vessels travel across the back of the wrist to supply blood to the back of the hand, fingers and thumb.
Bursae of the Hand
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that decrease friction between tendons and bone or skin. They contain special cells called synovial cells that secrete a lubricating fluid.
Hand & Wrist Conditions
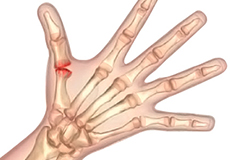
Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis and the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis. Arthritis affects various joints in the body and the arthritis in the hand affects the joint at the base of the thumb. Arthritis may also affect the joints of other digits.
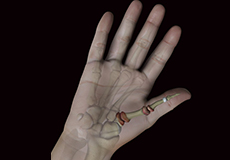
Arthritis of the Thumb
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis. The most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis that affects the joint at the base of the thumb. Thumb arthritis is more common in women than men, and usually occurs after the age of 40 years.

De Quervain's Tendinosis
Inflammation and swelling of the tendon sheaths put pressure on the adjacent nerves and leads to pain and numbness in the thumb side of the wrist. Strain on these tendons can cause swelling and irritation, and lead to a condition called De Quervain's tenosynovitis, which is characterized by inflammation. The condition is also referred to as De Quervain’s tendinitis, De Quervain’s tendinosis, De Quervain’s syndrome or De Quervain’s disease.
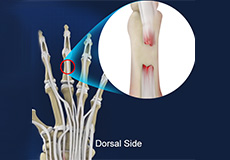
Extensor Tendon Injuries
Tendons are bands of tissue connecting muscles to bones. The extensor tendon is a strong, smooth cord that connects finger bones to muscles in the hand. Extensor tendons are located just under the skin, directly on the bone, on the back of the hand and fingers. They allow you to open your hands and move or straighten your wrist, fingers, and thumb.
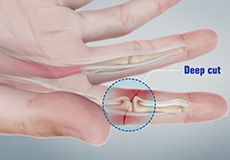
Flexor Tendon Injuries
Tendons are bands of fibrous connective tissue that connect muscles to bone. Tendons aid in the movement of the fingers, hand and all other body parts.
Finger Sprain
Injuries that involve tearing or stretching of the ligaments of your fingers are termed as sprains. Sprains in the fingers are most often caused from a fall when you extend your arms to reduce the impact of the fall, or from overuse or repetitive activity of the thumb such as with texting.

Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion cysts are swellings that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of wrists or hands. They can be found either at the top of the wrist, palm side of the wrist, end joint of a finger or at the base of a finger. A ganglion cyst is not cancerous and will not spread to the other parts of the body. It looks like a water balloon on a stalk and contains a clear fluid or jelly material. Ganglion cysts can be found in people of all ages.
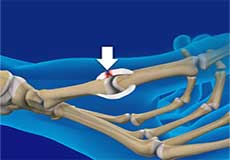
Gamekeeper's Thumb
Gamekeeper's thumb, also known as skier's thumb, is a tear of the ulnar collateral ligament, a band of tissue that supports the joint at the base of the thumb.
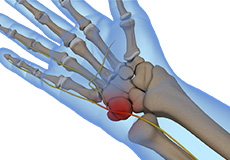
Guyon's Canal Syndrome
Guyon’s canal syndrome refers to compression of the ulnar nerve while it passes from the wrist into the hand through a space called the ulnar tunnel or Guyon’s canal.
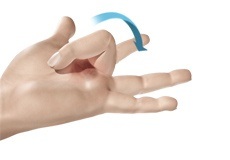
Trigger Finger
Inflammation in the tenosynovium leads to a condition called trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis or flexor tendonitis, where one of the fingers or thumb of the hand is caught in a bent position. The affected digit may straighten with a quick snap, like pulling and releasing the trigger on a gun, hence the name trigger finger.
Wrist Injuries
The wrist is a commonly injured joint in the body. Problems include sprains and strains as well as fractures that can occur with lifting and carrying heavy objects, while operating machinery, bracing against a fall, or from sports-related injuries.
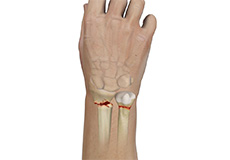
Wrist Injuries and Conditions
Wrist injuries commonly occur due to falls or certain sports and activities that involve repetitive use or excessive stress or strain on the wrists. These include gymnastics, basketball, working on an assembly line, or typing. Some wrist conditions have no clear cause.
Wrist Pain
Wrist pain is defined as any ache or discomfort in the wrist. The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm. The bones meet to form multiple large and small joints. A trauma or injury to one or more of these bones results in wrist pain.
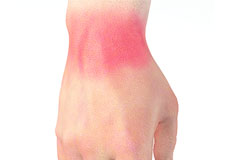
Wrist Sprain
Injuries caused due to stretching or tearing of the ligaments in the wrist are called wrist sprains. Sprains can range from mild to severe, based on the extent of injury to the ligament.
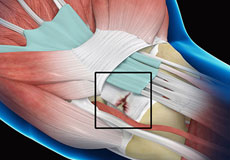
Wrist Ligament Tear and Instability
A ligament is a strong, flexible band of fibrous tissue. The wrist has many ligaments that help to keep the wrist bones in proper position providing stability to the joint. A torn ligament causes the wrist bones to move out of their position, which in turn leads to wrist instability as the sprained (torn) ligament can no longer support the wrist bones.


